This is the final post in the infertility series. Thank you so much for joining the conversation ladies, the feedback has been amazing and I'm glad that you've found the series and other posts useful.
Tubal factor infertility can also be caused by Endometriosis when endometrial tissue grows in the tubes thereby causing a blockage, previous surgery of the Fallopian tubes,treatment of ectopic pregnancies (a pregnancy growing in the Fallopian tubes or anywhere else outside the womb) and Fibroids growing in the Fallopian tubes.
Diagnosis of Tubal factor Infertility.
The main symptom women usually report is difficulty conceiving.Besides taking a complete history, baseline blood tests and also screening for sexually transmitted infections,the two definitive tests used to diagnose tubal factor infertility are:
Laparoscopy-using a small camera to view the Fallopian tubes OR
Hysterosalpingogram(HSG)- An Xray in which a dye is passed from the vagina into the womb and through the fallopian tubes to check for any blockages or damage.
Treatment of Tubal factor Infertility
Treatment is usually either by surgery to attempt to repair the damage or remove scar tissue or IVF. Over the years IVF has become the main stay of treatment however each option has to be clearly discussed with a fertility specialist who will help guide decision making.
Tubal factor infertility is quite common and the most common cause is PID which in turn is commonly caused by Chlamydia and Gonorrhoea in Nigeria
Are you sexually active? when was the last time you had a sexual health screen? Has your partner had a sexual health screen?
Are you pregnant? have you had a sexual health screen?
Whilst HIV is important, it is not the only sexually transmitted disease, evidence has shown that women are less likely to have any symptoms of chlamydia and Gonorrhoea. Besides contributing significantly to Infertility or subfertility, they can also have serious and life threatening consequences for unborn children.
Why don't you start the new week by going for a sexual health check, most common STIs can be treated but you will never know unless you take control and find out!
Thank you for sticking through the series whether or not it relates to you. It is important to stress that this series was by no means exhaustive. I decided to pick the most common topics for discussion.
This month is fertility awareness month, have you been affected by infertility? I would like to hear from you.
Don't forget to comment, subscribe and most importantly Share! you never know who might need this...
This week we will be discussing tubal factor infertility-basically this is infertility caused by damaged fallopian tubes.
The fallopian tubes are a pair of tubes leading from the ovaries to the womb, they enable the passage of released eggs to the womb, it is in this tube that the egg is usually fertilized by the sperm.
Tubal factor infertility is estimated to affect about 20- 25% of couples seeking fertility treatment worldwide. In Sub-Saharan Africa, tubal factor remains unofficially one of the leading cause of infertility due to pelvic inflammatory disease- a complication of sexually transmitted infections.
Infertility or sub fertility can occur when the Fallopian tubes are blocked(one or both), scarred or damaged in other ways. Tubal damage prevents the ovaries from travelling smoothly through the Fallopian tubes.
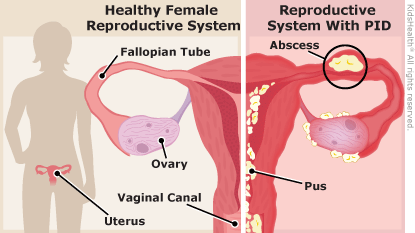
Pelvic inflammatory Disease
PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs. It is a very serious complication of sexually transmitted diseases in women and it can lead to irreversible damage of the Fallopian tubes. It is deemed to be the PRIMARY preventable cause of infertility as STDs can be treated. PID occurs when bacteria crosses from the vagina and ascends up the reproductive tract. Chlamydia and gonorrhea account for nearly 90% of PID cases. Whilst there is a lot of awareness about HIV and Hepatitis; a lot of women are not aware of other sexually transmitted infections that can affect fertility. What also causes a delay in diagnosis and treatment is the lack of symptoms in women unlike in men.
Chlamydia is the most common curable STI worldwide, it can generally present with no symptoms, approximately 50% of infected males and 80% of infected females show no symptoms (Nwadike 2015). It is often unrecognized and poorly treated as a result. This bacteria can ascend the reproductive tract resulting in PID and consequently lead to chronic pelvic pain, Ectopic pregnancy or Infertility.
Given the nature of this bacteria, screening programmes have been set up in developed countries to ensure that chlamydia is detected and adequately treated to prevent future complications. It is recommended that sexually active women under age 25 undergo annual screening and older women with multiple sexual partners or new partners undergo screening too.In studies looking at different population groups within Nigeria, it was mostly found in people aged 20-29.
Gonorrhoea is the second most common curable STI, it predominantly affects young people with a peak incidence between 20-24 in males and 16-19 in females(much lower!). It is also a leading cause of PID occurring when the bacteria ascends the reproductive tract. Whilst this bacteria can contribute to tubal infertility it can also lead to a severe infection in unborn babies,early labour or even stillbirths.
Symptoms of PID
Infertility or sub fertility can occur when the Fallopian tubes are blocked(one or both), scarred or damaged in other ways. Tubal damage prevents the ovaries from travelling smoothly through the Fallopian tubes.
Pelvic inflammatory Disease
PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs. It is a very serious complication of sexually transmitted diseases in women and it can lead to irreversible damage of the Fallopian tubes. It is deemed to be the PRIMARY preventable cause of infertility as STDs can be treated. PID occurs when bacteria crosses from the vagina and ascends up the reproductive tract. Chlamydia and gonorrhea account for nearly 90% of PID cases. Whilst there is a lot of awareness about HIV and Hepatitis; a lot of women are not aware of other sexually transmitted infections that can affect fertility. What also causes a delay in diagnosis and treatment is the lack of symptoms in women unlike in men.
Chlamydia is the most common curable STI worldwide, it can generally present with no symptoms, approximately 50% of infected males and 80% of infected females show no symptoms (Nwadike 2015). It is often unrecognized and poorly treated as a result. This bacteria can ascend the reproductive tract resulting in PID and consequently lead to chronic pelvic pain, Ectopic pregnancy or Infertility.
Given the nature of this bacteria, screening programmes have been set up in developed countries to ensure that chlamydia is detected and adequately treated to prevent future complications. It is recommended that sexually active women under age 25 undergo annual screening and older women with multiple sexual partners or new partners undergo screening too.In studies looking at different population groups within Nigeria, it was mostly found in people aged 20-29.
Gonorrhoea is the second most common curable STI, it predominantly affects young people with a peak incidence between 20-24 in males and 16-19 in females(much lower!). It is also a leading cause of PID occurring when the bacteria ascends the reproductive tract. Whilst this bacteria can contribute to tubal infertility it can also lead to a severe infection in unborn babies,early labour or even stillbirths.
Symptoms of PID
If you do experience symptoms, commonly reported symptoms include:
- Lower abdominal pain
- Heavy vaginal discharge most often with an unpleasant smell
- Pain or bleeding during intercourse
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding between periods
- Painful or difficult urination
- Fever often with chills
Tubal factor infertility can also be caused by Endometriosis when endometrial tissue grows in the tubes thereby causing a blockage, previous surgery of the Fallopian tubes,treatment of ectopic pregnancies (a pregnancy growing in the Fallopian tubes or anywhere else outside the womb) and Fibroids growing in the Fallopian tubes.
 |
| RCHSD.ORG |
Diagnosis of Tubal factor Infertility.
The main symptom women usually report is difficulty conceiving.Besides taking a complete history, baseline blood tests and also screening for sexually transmitted infections,the two definitive tests used to diagnose tubal factor infertility are:
Laparoscopy-using a small camera to view the Fallopian tubes OR
Hysterosalpingogram(HSG)- An Xray in which a dye is passed from the vagina into the womb and through the fallopian tubes to check for any blockages or damage.
Treatment of Tubal factor Infertility
Treatment is usually either by surgery to attempt to repair the damage or remove scar tissue or IVF. Over the years IVF has become the main stay of treatment however each option has to be clearly discussed with a fertility specialist who will help guide decision making.
Tubal factor infertility is quite common and the most common cause is PID which in turn is commonly caused by Chlamydia and Gonorrhoea in Nigeria
Are you sexually active? when was the last time you had a sexual health screen? Has your partner had a sexual health screen?
Are you pregnant? have you had a sexual health screen?
Whilst HIV is important, it is not the only sexually transmitted disease, evidence has shown that women are less likely to have any symptoms of chlamydia and Gonorrhoea. Besides contributing significantly to Infertility or subfertility, they can also have serious and life threatening consequences for unborn children.
Why don't you start the new week by going for a sexual health check, most common STIs can be treated but you will never know unless you take control and find out!
Thank you for sticking through the series whether or not it relates to you. It is important to stress that this series was by no means exhaustive. I decided to pick the most common topics for discussion.
This month is fertility awareness month, have you been affected by infertility? I would like to hear from you.
Don't forget to comment, subscribe and most importantly Share! you never know who might need this...

Comments
Post a Comment